|
LIONS
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
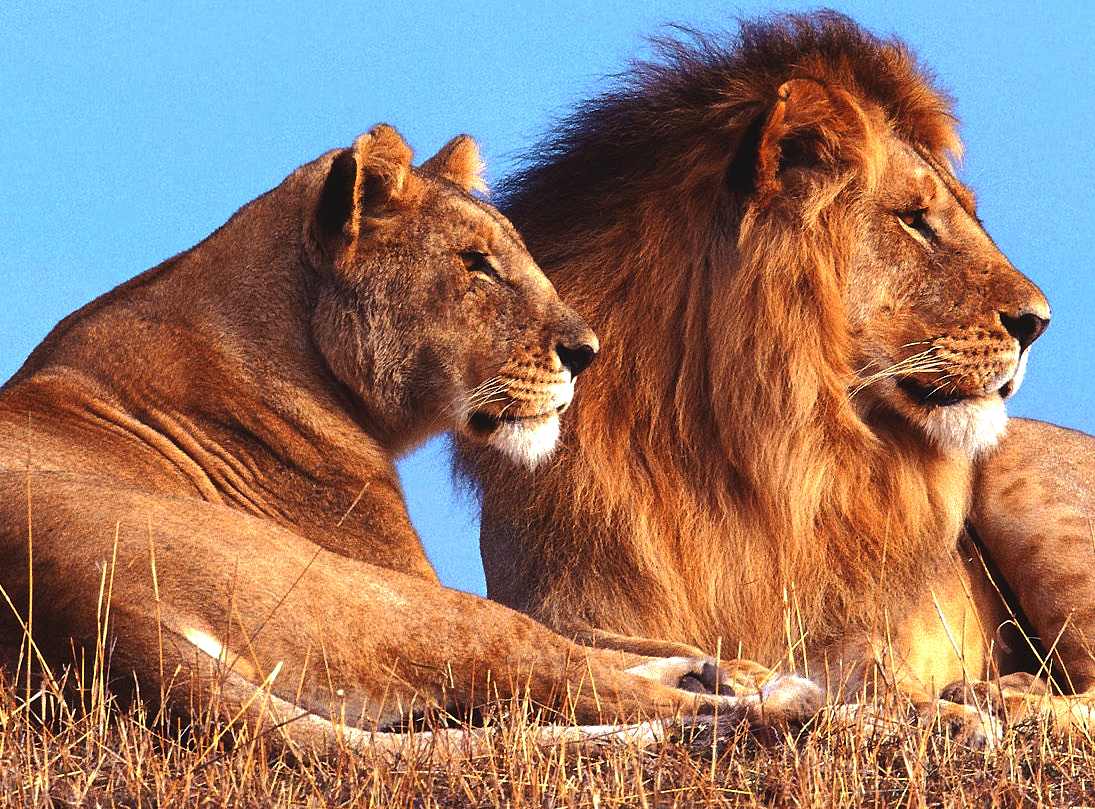
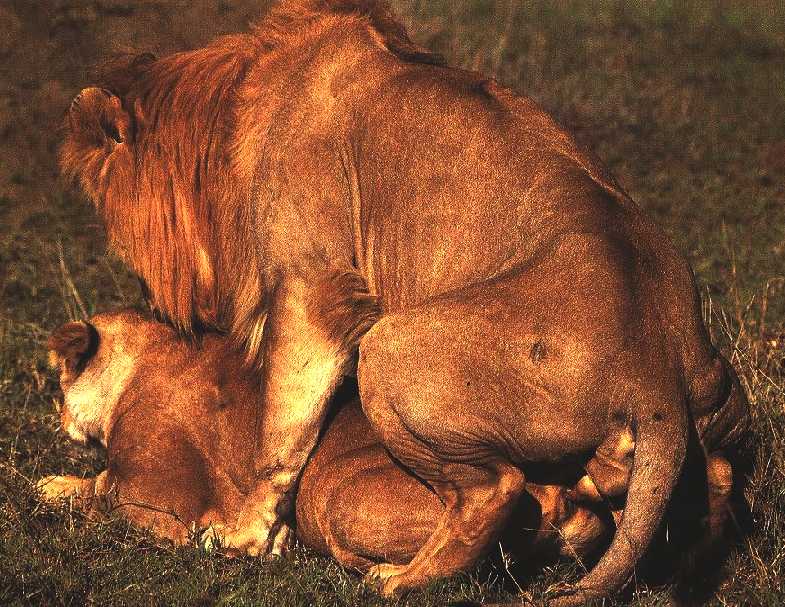
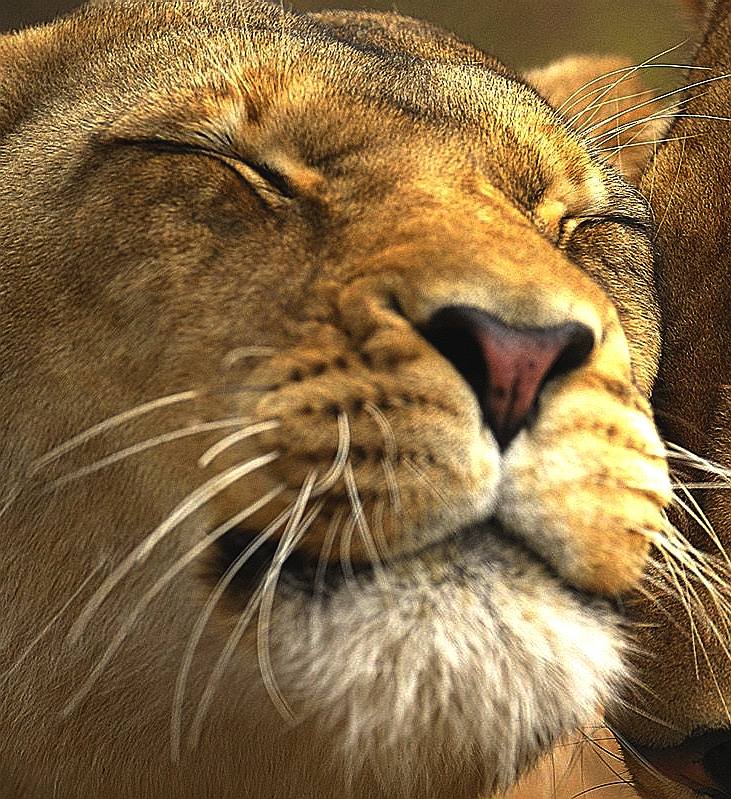
The Lion (Panthera leo) is a mammal of the family Felidae and one of four "big cats" in the panthera genus. The lion is the second largest living cat, after the tiger. The male lion, easily recognized by his mane, weighs between 150-225 Kg (330-500 lb) and females average 120-150 kg (260-330 lb) [1]. In the wild, lions live for around 10–14 years, while in captivity they can live over 20 years. To reproduce, the lions mate for long periods of time.
Oh somebody please turn the lights out
Population and distribution
In historic times the habitat of lions spanned much of Eurasia, ranging from Portugal to India, and all of Africa. Around the beginning of the current era they died out from Western Europe and since the 2nd century, the lion has disappeared from Europe. Between the late 19th century and early 20th century they also became extinct from North Africa and Middle East. Now, most of the population lives in Central Africa, and their numbers are rapidly decreasing, estimated as between 16,000 and 30,000 living in the wild, down from an estimated 100,000 in the early 1990s. The population is even more in jeopardy, because the remaining populations are often geographically isolated from each other, which causes inbreeding.
The last remnant of the Asiatic Lion (subspecies Panthera leo persica), which in historical times ranged from Turkey to India through Iran (Persia) and from Caucasus to Yemen, lives in the Gir Forest of northwestern India. About 300 lions live in a 1412 km˛ (558 square miles) sanctuary in the state of Gujarat.
Lions had become extinct in Greece, their last European outpost, by 100. Other extinct subspecies are the Cape Lion, the European Cave Lion (subspecies Panthera leo spelaea) which coexisted with humans throughout the last Ice Age, and the American lion (subspecies Panthera leo atrox), a close relative of the European cave lion (not to be confused with the mountain lion or puma).
Come here you I want to whisper in your ear
Manes
The first lions were presumed to have been maneless. Until around 10 000 years ago, maneless forms seem to have persisted in Europe, and possibly the New World. The maned form may have appeared c. 320 000–190 000 years ago. This maned form may have had a selective advantage that enabled it to expand to replace the range of earlier maneless forms throughout Africa and western Eurasia by historic times. The mane has evolved due to sexually selective pressure driving the trait to an exaggerated point where it no longer serves any other function. The trait has reached the point where cost of maintaining the mane has begun to outweigh its benefits. In fact, lions with particularly large manes often have trouble with thermoregulation.
In the past scientists believed that the "distinct" subspecific status of some subspecies could be justified by their external morphology, like the size of their mane. This morphology was used to identify them, like the Barbary lion and Cape lion. However, now it is known that various extrinsic factors influence the colour and size of a lion’s mane, like the ambient temperature. The cooler ambient temperature in e.g. European and North American zoos can result in heavy mane. Therefore, the heavy mane is an inappropriate marker for identifying subspecies.
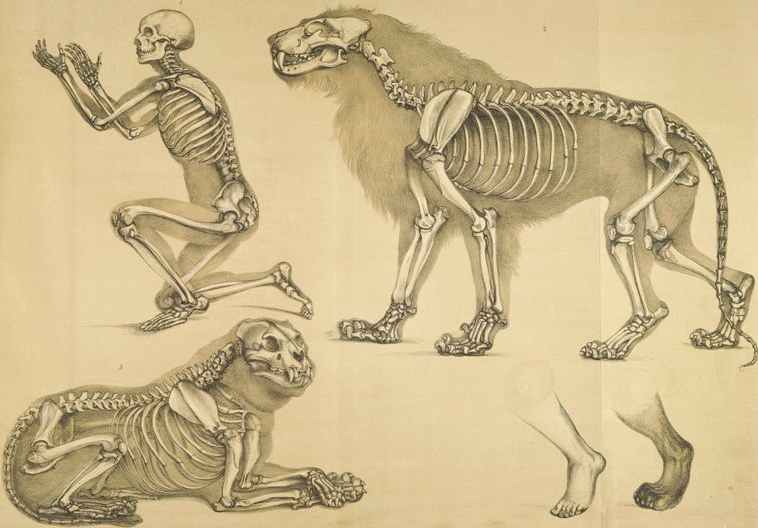
Comparative view of the human and lion frames, c1860
Behavior
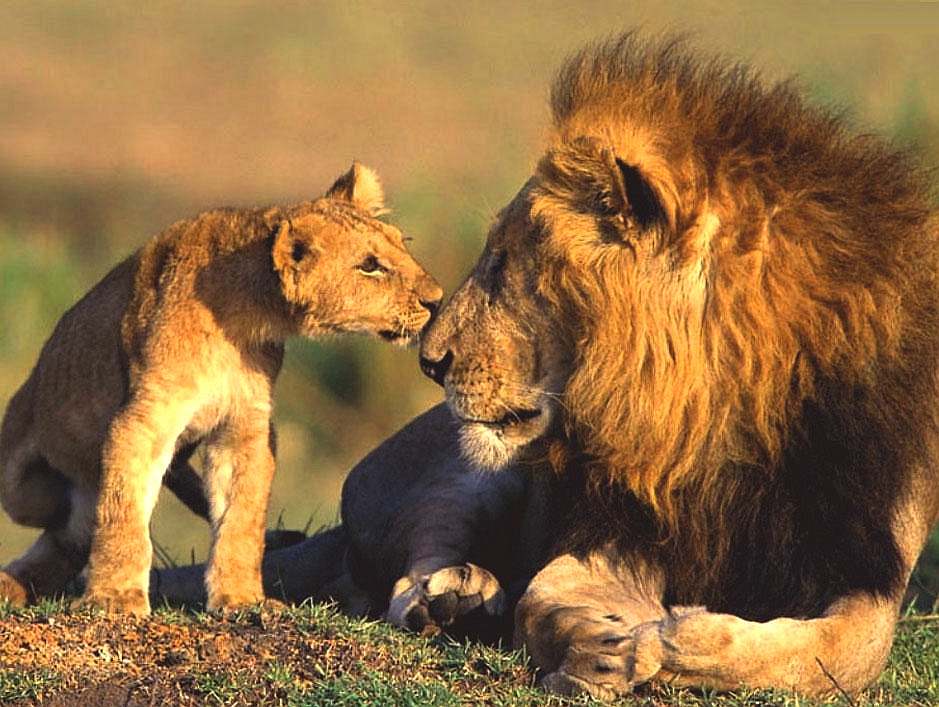
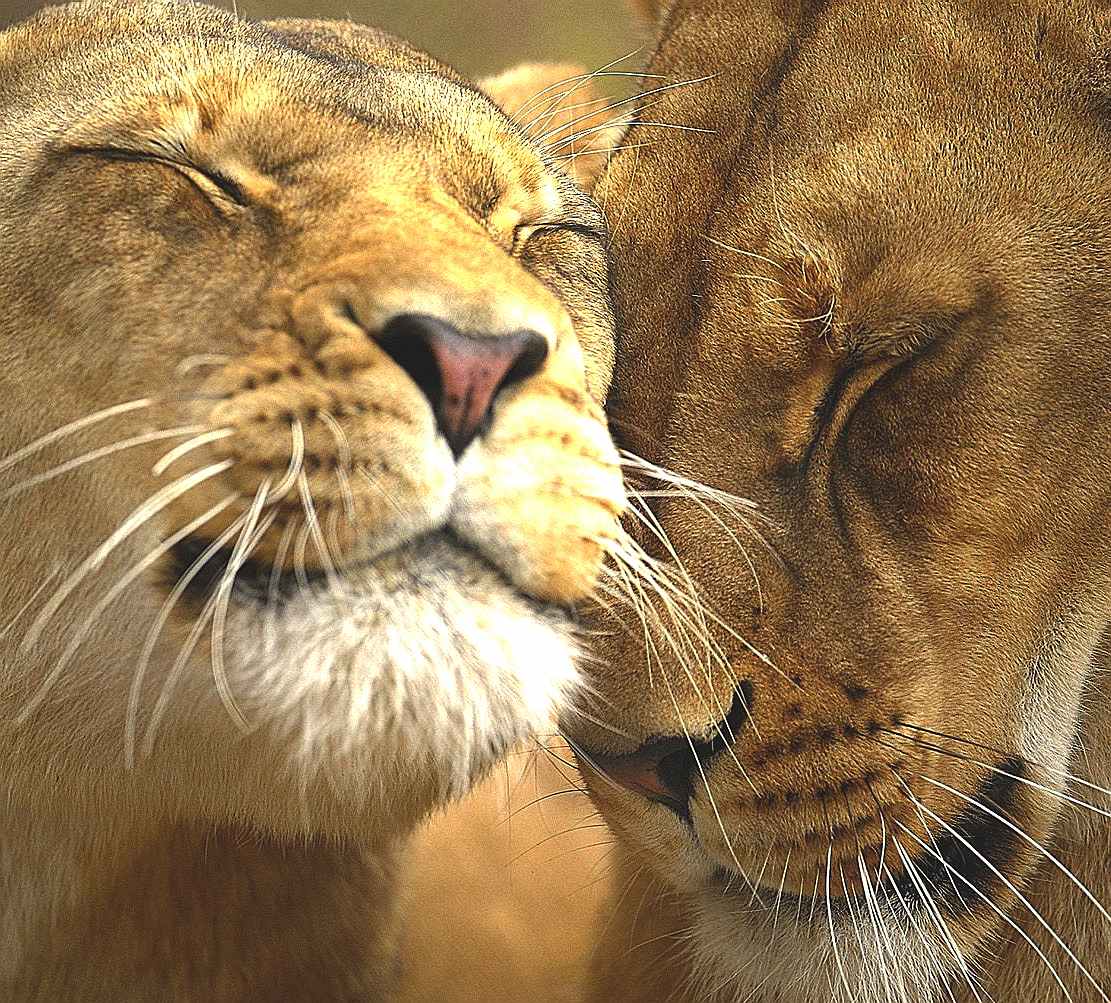
Lions are predatory carnivores who live in family groups, called prides. The family consists of related females, their cubs of both sexes, and one or more males (often brothers) who mate with the adult females. Although it was once thought that females did most of the hunting in the pride, it is now known that males contribute to hunting. All male lions display hunting skills while they have yet to capture a pride of their own. Even males who have captured a pride of their own may still hunt. The frequency of hunting by male lions who have captured a pride is influenced by the terrain and available prey. Males in more wooded environments hunt for themselves far more frequently than males on the open savannah. Additionally, males appear to prefer buffalo as prey where females appear to prefer smaller prey such as the Blue Wildebeest and zebra. Regardless of who kills the prey, the male usually eats his fill first with the rest of the pride staying at a respectful distance.
Do you reckon that herd of wildebeest are coming this way?
Both males and females will defend the pride against intruders. Typically, males will not tolerate outside males, and females will not tolerate outside females. Males are expelled from the pride or leave on their own when they reach maturity. The male lion is a superb master and defender of his pride and territory.
When a new male (or a coalition) takes over a pride and ousts the previous master(s), the conquerors often kill any remaining cubs. This is explained by the fact that the females would not become fertile and receptive until the cubs grow up or die. The male lions reach maturity at about 3 years of age and are capable of taking over another pride at 4-5 years old. They begin to age (and thus weaken) at around 8. This leaves a short window for their children to be born and mature — the fathers have to procreate as soon as they take over the pride.
Sometimes a female may defend her and the ousted male's children from the new master, but such actions are rarely successful.
Kevin Richardson, Lion whisperer
Attacks on humans
While a hungry lion may occasionally attack a human that passes near, some (usually male) lions seem to seek out human prey. Some of the more publicized cases include the Tsavo maneaters and the Mfuwe man-eater. In both cases the hunters who killed the lions wrote books detailing the lions' "careers" as man-eaters. In folklore, man-eating lions are sometimes considered demons.
The Mfuwe and Tsavo incidents did bear some similarities. The lions in both the incidents were all larger than normal, lacked manes and seemed to suffer from tooth decay. Some have speculated that they might belong to an unclassified species of lion, or that they may have been sick and could not have easily caught prey.
There have also been recorded attacks on humans by lions in captivity; tigers are statistically much more likely to attack humans in captivity. Wild lions are also much less likely to attack humans than wild tigers are.
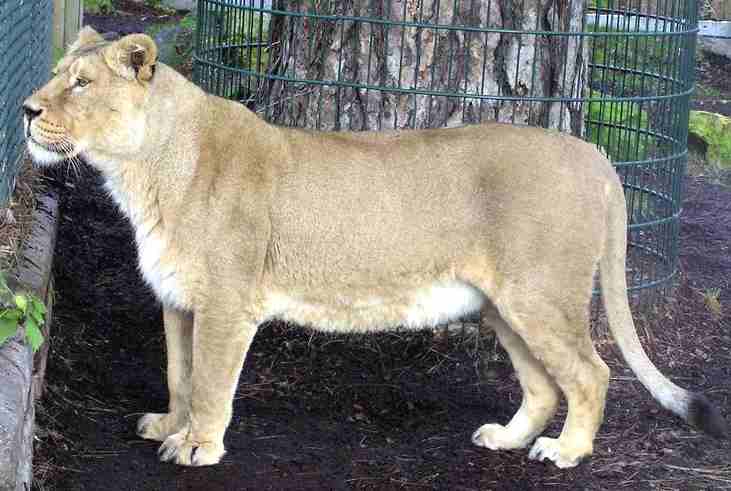
Asiatic Lioness Panthera leo persica, name MOTI, born in Helsinki Zoo (Finland) October 1994, arrived Bristol Zoo (England) January 1996. The Gir Forest in India is the natural home of the Asiatic lion
Taxonomy
Subspecies
The major differences between lion subspecies are location, mane appearance, size and distribution. However some of the forms listed below are debatable. Genetic evidence suggests that all modern lions derived from one common ancestor only circa 55,000 years ago. Therefore most sub-Saharan lions could be considered a single subspecies Panthera leo leo.
Most scientists today recognise subspecies (not all named here are considered valid by all scientists).
Lion: "Sit still woman" - Lioness: "You smooth talker you"
Dad, mind if I borrow the car tonight?
Besides these subspecies there are also some prehistoric ones.
Christian the pet Lion from Harrods meets John Rendall and Ace Berg after release into the wild
The face that launched a thousand kisses, umm that warthog tasted good
Variations
White lions
Although they are not often heard of due to their rarity, white lions do exist, in Timbavati, South Africa. There is a recessive gene in white lions that gives them their unusual color (many white tigers with this same gene are bred for zoos and animal shows). A white lion has a disadvantage when it comes to hunting: it can be given away by its color, unlike the regular lion which blends in with its surroundings.
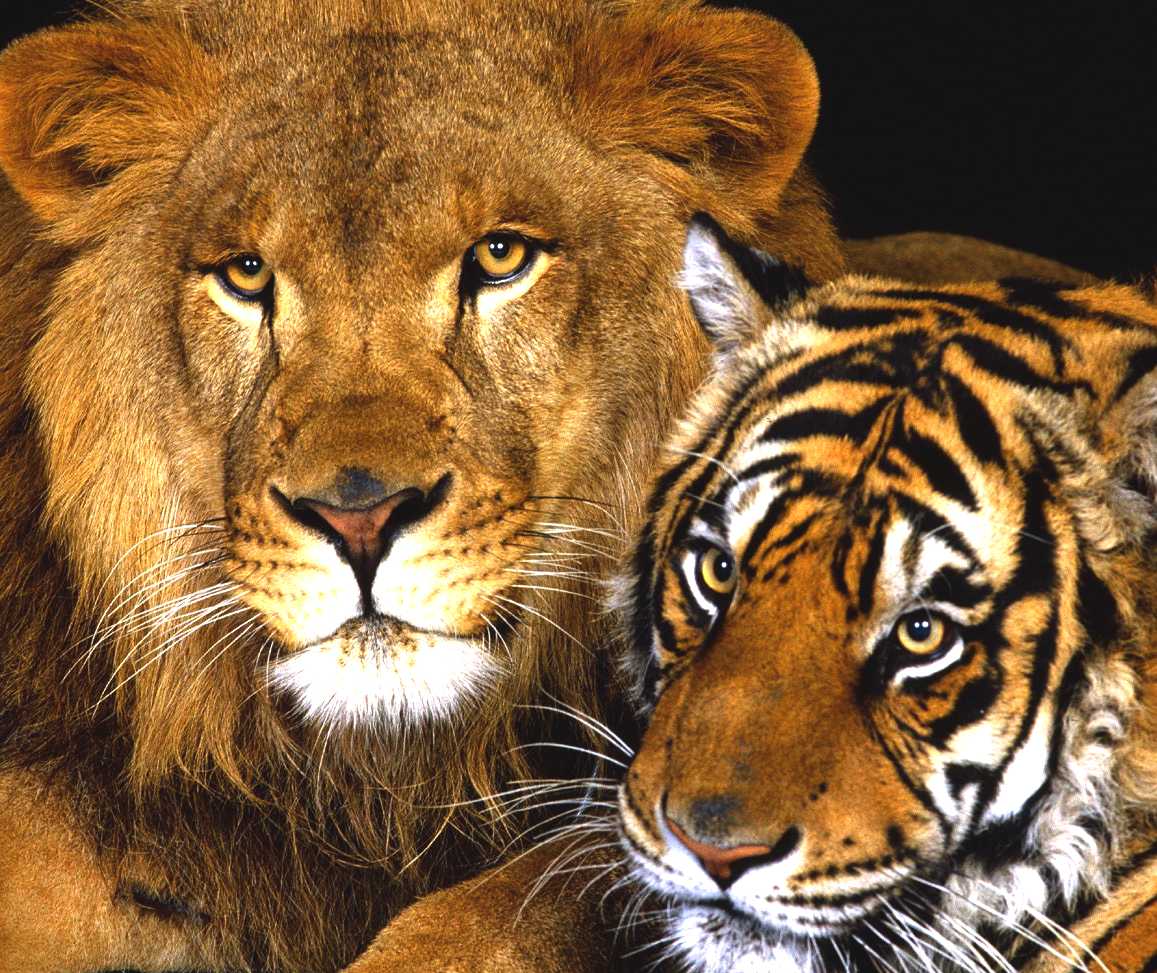
Cross-breeding with tigers
Lions have also been known to breed with their close counterparts, tigers (most often Amur), while in captivity to create interesting mixes. These two new breeds are called ligers and tigons.
I thought so too, are there seconds?
The liger originates from mating a male lion and a tigress. Because the lion passes on a growth-promoting gene, but the corresponding growth-inhibiting gene from the female lion is not present, ligers are larger than either parent. It is said that ligers do not stop growing and will grow constantly through their lifespan, until their bodies cannot sustain their huge size any longer, reaching up to half a tonne. Ligers share some qualities of both their parents (spots and stripes) however they enjoy swimming, a purely tiger activity, and they are always a sandy color like the lion. Male ligers are sterile, but female ligers are often fertile.
The tigon is a cross between the lioness and the male tiger. Because the male tiger does not pass on a growth-promoting gene and the lioness passes on a growth inhibiting gene, tigons are often relatively small, only weighing up to 150 kilograms (350 lb), which is about 20% smaller than lions. They can best be described as "housecat-like" in appearance, although with round ears. Like male ligers, male tigons are sterile, and they all have both spots and stripes, with yellow eyes. Tigons are not as common as ligers because they are more difficult to produce since male tigers are less attracted to lionesses because of their smaller size and are thought to have difficulty with recognizing lioness breeding cues.
Female ligers and female tigons are fertile and can produce offspring if mated to either a pure-bred lion or a pure-bred tiger. Such inter-breeding was a practice earlier, but has been stopped now.
If they can do it why can't we - peace to all men on earth
Lions in culture
Lions are recurring symbols in the coat of arms of royalty and chivalry, particularly in the UK, where the lion is also a national symbol of the British people, and in Ethiopia, where it is a symbol of the Monarchy. Lions appear in the art of China, even though lions have never lived in China. No animal has been given more attention in art and literature. C.A.W. Guggisberg, in his book Simba, says the lion is referred to 130 times in the Bible, for example in 1 Peter 5:8 where the Devil is compared to a roaring lion:
The lion can also be found in stone age cave paintings.
Lions in art
Lions have been widely used in sculpture and statuary to provide a sense of majesty and awe, especially on public buildings, including:
Lions in literature
Lions in media
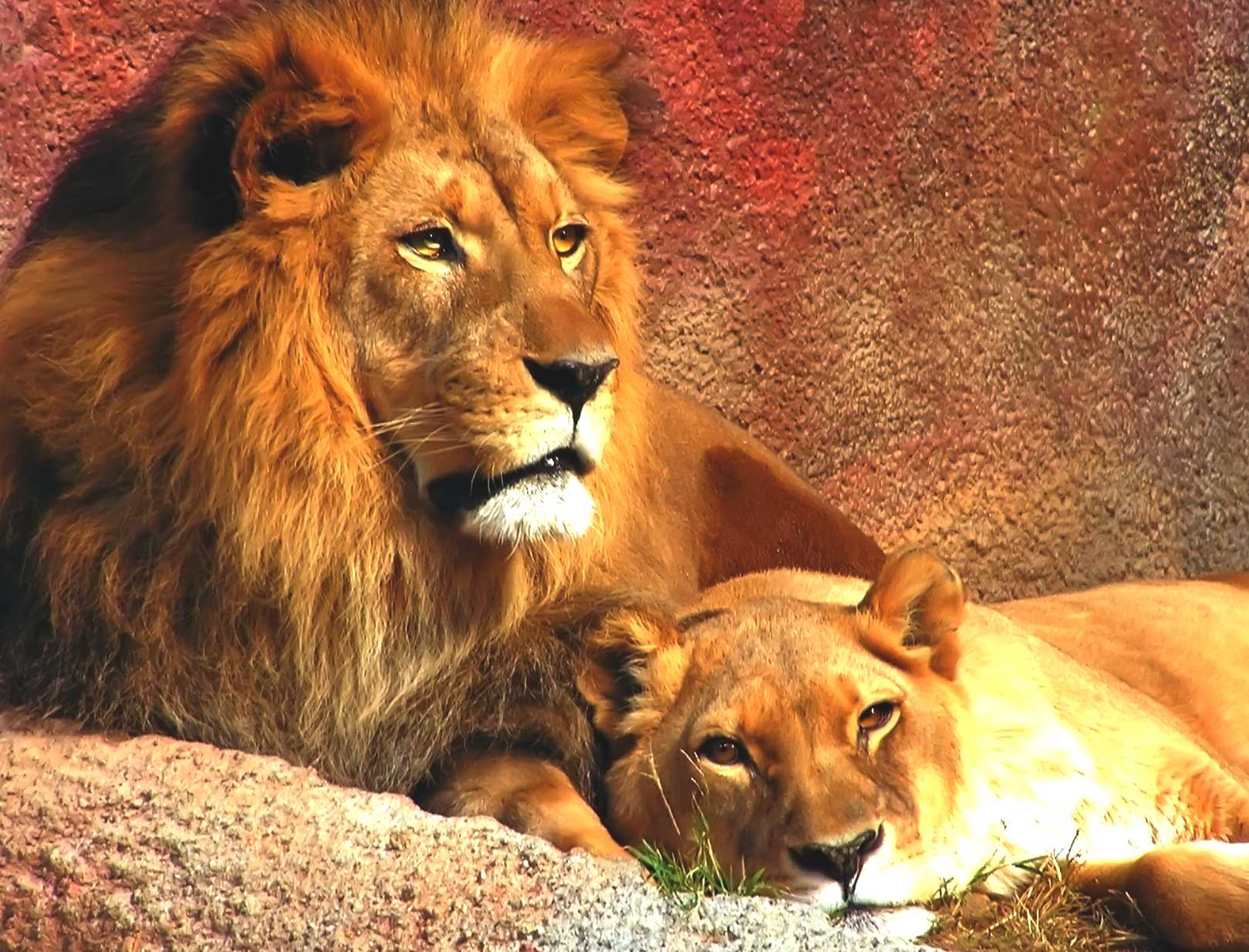
Lovely photograph of a pair of lions resting: "Hey, give us a break"
Lions in heraldry
The lion is a common image in heraldry, traditionally symbolizing bravery, valor and strength.
The following positions of heraldic lions are recognized: rampant, guardant, reguardant, passant, statant, couchant, salient, sejant, dormant.
The image of lion appears on many flags, coats of arms and emblems. For example, it symbolises the Sinhala people (Sinhalese Singha = Lion). Local folklore tells of Prince Vijaya, the first of the Sinhalese kings, as being the son of Sinhabahu, who was fathered by a lion.
I don't know what's in the water, but it sure tastes good
REFERENCE and LINKS:
Lion v man meeting
POPULAR MAMMALS:
Lions bring down a hippo
World Cup Willie the mascot of the FIFA World Cup in 1966
Index to navigate Animal Kingdom:-
Learn how to carve a lion in wood by clicking on the picture above
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This website is Copyright © 1999 & 2015 Max Energy Limited, an environmental educational charity working hard for world peace. The names Solar Navigator™, Miss Ocean™ and Utopia Tristar™ are trademarks. All other trademarks are hereby acknowledged.
|