|
WEALDEN IRON INDUSTRY
|
|||||||||||||||
|
It is hard to picture the former iron industry in today's countryside of small fields, woodlands and steep, narrow, gill valleys. But in this landscape exist all the necessary raw materials that allowed iron to be smelted for over 2,000 years. There were no planning laws in those days and no planning officers to put a spanner in the works.
Furnace Pond
The Wealden geology of sands and clays yielded the iron ore, as well as the stone and brick to build the furnaces; the woodland provided the charcoal fuel; and the numerous small streams and valleys ensured water power for the bellows and hammers of the forges and furnaces.
For two periods - in the first two centuries of the Roman occupation, and during Tudor and early-Stuart times - the Weald was the main iron-producing region in Britain. Julius Caesar first drew attention to iron being produced in the coastal parts of Britain. Archaeologists have found evidence of iron working from the late Iron Age at sites near Crowhurst and Sedlescombe in the south-eastern High Weald.
When the Romans invaded in AD 43, they found a well-established local tradition of iron making, using small, clay bloomery furnaces. With growing markets generated by the building of towns, villas and farms, the Romans encouraged this native industry. Sites from the period have been found all over the eastern part of the High Weald.
The 'Classis Britannica', or British Fleet, an imperial supply organization as well as a navy, took a strategic role in iron production. It managed several large smelting sites in the area around Hastings, such as one at Beauport Park, near Battle. This may have produced as much as 30,000 tonnes of iron over 130 years, and a substantial bathhouse was built there for some of the workforce. We know little about iron making in the Weald in Saxon times, and the industry receives only one mention in the Domesday Book for Sussex, at a location near East Grinstead.
Iron making furnace in blast
However, during the Middle Ages iron production grew steadily, concentrated more in the northern part of the Weald. Accounts have survived from 14th-century works at Tudeley in Kent, and excavations have confirmed medieval references to iron makers in Crawley and near Horsham. Towards the end of the period, water-power began to be used for forging iron, heralding the introduction, in 1496, of the blast furnace.
Introduced from northern France, and operated by skilled, immigrant workers, the blast furnace was a much larger, and more permanent structure than the bloomery; and instead of a few kilos of iron being made, daily output was nearer a tonne.
More ore and charcoal were required, and the need to operate the bellows by waterpower, instead of by hand, meant that ponds had to be created to store the water. In addition, the higher temperatures in the furnace meant that a different type of iron was being produced. A second process ˜ the forge, with its own pond and supply of charcoal - was needed to refine the iron.
By the mid-16th century there were 50 furnaces and forges, and that number had doubled 25 years later. All over the Weald, the iron industry was having an effect, with large numbers of people employed in digging ore, cutting wood and transporting both raw materials and products.
Most furnaces made "sows", or lengths, of iron for refining, but from the 1540s a small number began to make cast-iron cannon, a product that grew to be a profitable, and sometimes illegal, export. Improvements in house design led to the building of chimneys, and the need for iron fire-backs to protect the brickwork. Many Wealden farmhouses contain examples of these decorative and functional plates. In several Wealden churches there are examples of iron memorials. The oldest is in Burwash, dating from the 1530s, while Wadhurst church has over 30, dating from the early-17th to the late-18th centuries.
As competition from imported iron increased, the Wealden ironmasters began to concentrate increasingly on gun founding, and examples can be found all over the world, wherever Britain fought or traded. Eventually, the onset of the Industrial Revolution took heavy industry north to the coalfields, and the last furnace in the Weald, at Ashburnham, closed in 1813.
So, where are the remains of iron production? Building stone was too valuable in the Weald to be left unused, so the works were dismantled, and the woods grew back over the former sites. Only the tell-tale waste, called slag, from the smelting process, and some of the hammer and furnace ponds are left to remind us of a once-great Wealden industry.
Iron ore pits
THE WEALDEN IRON RESEARCH GROUP - WIRG
The Wealden Iron Research Group was founded in 1968, by Henry Cleere and David Crossley, to update the pioneering work of Ernest Straker whose monograph, Wealden Iron, had been published in 1931. Starting off as a federation of local groups, it coalesced in the early 1970s under the leadership of the late Fred Tebbutt, a distinguished amateur archæologist, who became its first Chairman. Much of the early work of the group centred around the update of Straker's work, but it was soon realised that much lay undiscovered.
A survey of an area of the central Weald revealed a dense concentration of early iron smelting sites, or bloomeries, and this has acted as an incentive for future work. Experiments in making iron were started, and the group won the BBC's 'Chronicle' Award for Archæology in 1981. The publication, in 1985, of The Iron Industry of the Weald, by Cleere and Crossley, was the fulfilment of the group's initial aim, but many questions remained unanswered, and the group continues an active programme of research.
Text by Jeremy Hodgkinson of the Wealden Iron Research Group. Illustrations by Mike Codd, West Sussex County Council
The Wealden Iron Research Group (WIRG) website provides information on a wide range of the groups activities together with a general introduction to iron production in the Weald. The Weald has been identified as a key iron-producing region for the British Isles and it contains nearly 800 identified iron-making sites dating from the pre-Roman period up to the 19th century. The WIRG, established in 1968, has carried out a wide range of activities on the Weald. The website contains information on the group's research aims, meetings, excavations and other fieldwork together with details on how to become a member.
One of the key group activities is conducting a programme of experiments intended to replicate the bloomery smelting process used in the Weald during the Roman occupation. The website contains a highly detailed and well-illustrated section on these experiments together with details of the groups publications and annual bulletin of research. Aside from providing details on the WIRG itself, the website also contains a brief history of the iron industry in the weald from prehistory to nineteenth century.
The WIRG website is simply and consistently set out using frames and is via navigation a standardised side menu. The illustrations are clear, are captioned and linked to larger versions. The site also contains a number of links to related websites.
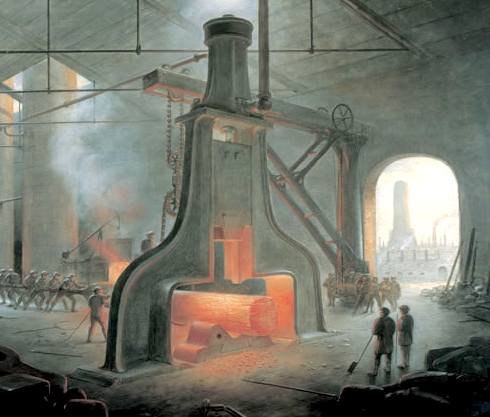
Nasmyth’s steam hammer of 1840 at work in 1871
How to join WIRG
Membership of WIRG is open to individuals, families and institutions, students and those of pensionable age, and includes a bi-annual Newsletter and the Wealden Iron Bulletin. Activities include a Field Group, which organises a programme of fieldwork in the autumn and winter, bi-annual meetings with visiting speakers, small-scale excavations, and a variety of other projects undertaken by its members. WIRG administers the Tebbutt Research Fund which awards small grants towards research into the Wealden iron industry.
The
current subscription rates in Sterling are:
You may find out more by emailing David Brown. Download an application form in PDF format by clicking HERE. Complete and post it to The Hon. Secretary WIRG, 2 West Street Farm Cottages, Maynards Green, HEATHFIELD, Sussex, TN21 0DG, with your cheque made payable (in sterling) to Wealden Iron Research Group. If you pay tax, you may wish to complete a Gift Aid form to help the Group reclaim your tax.
WIRG LINKS:
Early progress in the Melting of Iron
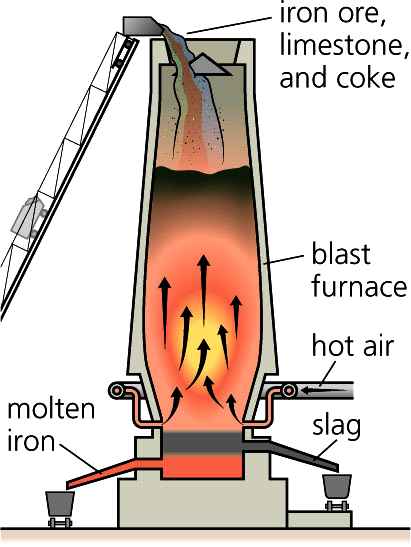
Schematic of modern iron making blast furnace
LINKS and REFERENCE
Tim Young (Exp Bloomery at St Fagans, Cardiff) Rievaulx
reconstructed medieval bloomery INAGINA Tranemo Sweden - experimental bloomery operation (in Swedish) Ancient
iron & Steel Industry in the Black Mountains (South of France) 'The Smelters Art' - Rockbridge Bloomery, Lee Sauders & Skip Williams
History and Archeology
The Making of the High Weald Sussex Archaeological Society The Sussex Weald CBA SouthEast Romans in Sussex Classis Britannica
Metallurgy and Smelting
Experimental Iron Smelting at Scatness Experimental Bloomery Site in Wales Whitehall Farm Roman Villa smelting experiments Experimental Iron Smelting at Rievaulx Historical Metallurgy Society Department of Materials Science, Oxford University
Museums / Educational
The Ironbridge Gorge Museums - Shropshire UK Sowley Ironworks, Hampshire Duddon Furnace, Cumbria The Real Wrought Iron Company The Wilkinson Family, Ironmasters
Sites outside UK
Forges du Saint Maurice, in Canada Saugus Furnace, Massachusetts, USA Hopewell Furnace, Pennsylvania, USA Maison de la Métallurgie et de l'Industrie de Liège (in French) Lapphyttan Ironworks - Sweden
SUSSEX INDEX A - Z
ARUNDEL CASTLE - WETLANDS WILDFOWL TRUST BEACHY HEAD - BELL TOOT (BELLE TOUT) LIGHTHOUSE CHIDDINGLY - HORSE SHOW and GYMKHANA CUCKMERE VALLEY - EXCEAT EAST
SUSSEX HERSTMONCEUX - CASTLE - CE SCHOOL - LINKS - FESTIVAL TWISSELLS MILL, OLD HEATHFIELD
Herstmonceux Electricity Generating Works Circa. 1900 - 1936 Links:
Introduction | Instructions | ISBN | Batteries | Boiler Room | Floor Plan | Ron Saunders
Industrial Revolution | Lime Park | Machinery | Map | Power House | Argus 1999
Public Supply | Roof Construction | Rural Supply | Sussex Express 1913 | Conclusion
Archaeology South East | East Sussex CC | English Heritage | SIAS | Sx Exp 1999
GENERAL HISTORY
MARITIME HISTORY
LINKS:
http://www.theguardian.com/
Anthropology
| Archaeology | Dinosaurs
| Evolution | Fossils
| Geology | Mammoths Meteorites
| Paleontology | Plate
Tectonics | Neanderthal Man
|
|||||||||||||||
|
This website is Copyright © 1999 & 2017 the Cleaner Oceans Club Ltd, is an environmental educational charity working hard for world peace. The names Bluebird™, Miss Ocean™, and SolarNavigator™ are registered trademarks. All other trademarks are hereby acknowledged.
|