|
WILLIAM BLIGH
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
HOME | BIOLOGY | FILMS | GEOGRAPHY | HISTORY | INDEX | INVESTORS | MUSIC | SOLAR BOATS | SPORT |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Vice-Admiral William Bligh, FRS, RN (9 September 1754 – 7 December 1817) was an officer of the British Royal Navy and colonial administrator. He is best known for the famous mutiny that occurred against his command, aboard HMAV (His Majesty's Armed Vessel) Bounty and the remarkable voyage he made to Timor, on the Bounty's launch, after being set adrift by the mutineers. Many years after the Bounty mutiny, he was appointed Governor of New South Wales, with a brief to clean up the corrupt rum trade of the NSW Corps. He had some success in his task but quickly faced opposition, which culminated in the Rum Rebellion led by Major George Johnston working closely with John Macarthur.
William Bligh
Although William Bligh was certainly not the vicious man portrayed in popular fiction, some claim his over-sensitivity and acid tongue damaged what would have otherwise been a distinguished career.
Early life
Bligh was born on September 9, 1754 to Francis and Jane Bligh (née Balsam) in Plymouth, although of a Cornish family. He was signed up for the sea at the age of seven in the same city. Whether he went to sea at this tender age is doubtful, as it was common practice to sign on a "young gentleman" simply in order to rack up the required years of service for quick promotion. In 1776, he was selected by Captain James Cook for the position of Sailing Master on the Resolution and accompanied Captain Cook in July 1776 on Cook's third and fatal voyage to the Pacific. He reached England again at the end of 1780 and was able to give further details of Cook's last voyage.
He married Elizabeth Betham, the daughter of a Customs Collector on 4 February 1781 and a few days thereafter he was appointed to serve on HMS Belle Poule as its master. Soon after this in August 1781 he fought in the Battle of Dogger Bank under Admiral Parker. For the next 18 months he was a lieutenant on various ships. He also fought with Lord Howe at Gibraltar in 1782. Between 1783 and 1787 he was a captain in the merchant service. In 1787 he was selected as commander of HMAV Bounty. He would eventually rise to the rank of Vice Admiral in the British Royal Navy.
Naval career
William Bligh's naval career consisted of a variety of appointments and assignments. A summary is as follows:
The voyage of the Bounty
In 1787, Bligh took command of the Bounty. He first sailed to Tahiti to obtain breadfruit trees, then set course for the Caribbean, where breadfruit was wanted for experiments to see if it would be a successful food crop for slaves there. The Bounty never reached the Caribbean, as mutiny broke out onboard, shortly after leaving Tahiti. In later years, Bligh would repeat the same voyage that the Bounty had undertaken and would eventually succeed in delivering the breadfruit to the West Indies. Bligh's mission may have introduced the Ackee to the Caribbean as well, though this is uncertain (Ackee is now called Blighia sapida in binomial nomenclature, after Bligh).
The voyage was difficult. After trying unsuccessfully for a month to round Cape Horn, the Bounty was finally defeated by the notoriously stormy weather and forced to take the long way around the Cape of Good Hope. That delay resulted in a further delay in Tahiti, as they had to wait 5 months for the breadfruit plants to mature enough to be transported. The 'Bounty' departed Tahiti in April 1789.
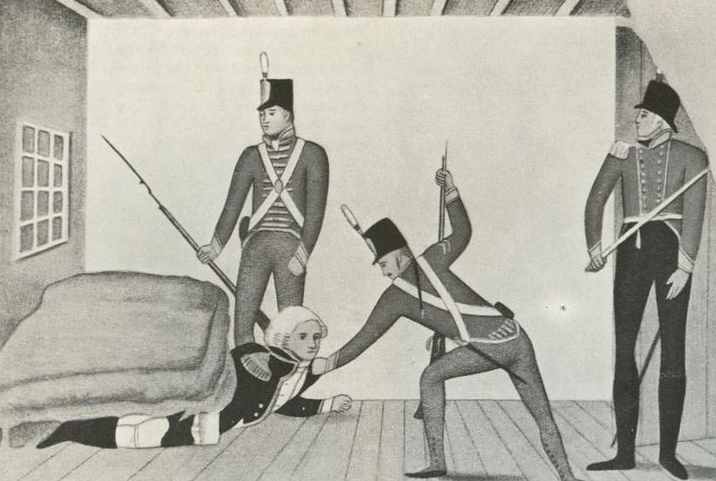
Propaganda cartoon of Bligh's arrest in Sydney in 1808 to try to show Bligh as being a coward
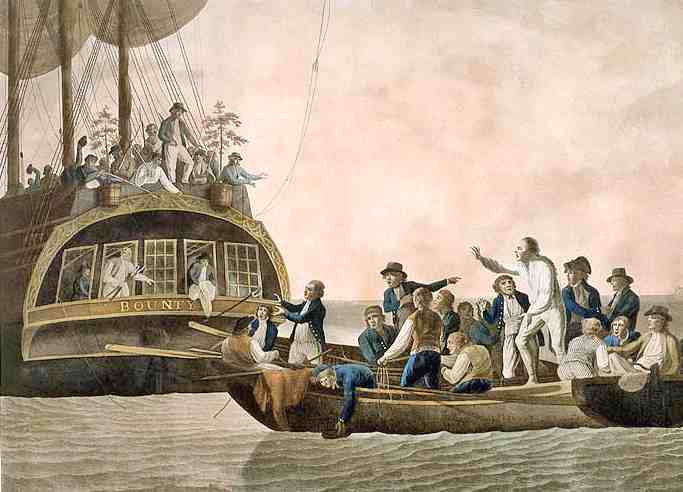
Since it was rated only as a cutter, the Bounty had no officers other than Bligh himself (who held only a lieutenancy), a very small crew, and no Marines to provide protection from hostile inhabitants during stops or enforce security on board ship. To allow longer uninterrupted sleep, Bligh divided his crew into three watches instead of two, and placed his protege Fletcher Christian — rated as a Master's Mate — in charge of one of the watches. The mutiny, which broke out during the return voyage on April 28, 1789, was led by Christian and supported by a quarter of the crew, who had siezed firearms during Christian's night watch and surprised and bound Bligh in his cabin. Despite their being in the majority, none of the loyalists seemed to have put up any significant struggle once they saw Bligh bound, and the ship was taken bloodlessly. The mutineers provided Bligh and the eighteen of his crew who remained loyal with a 23 foot (7 m) launch (so heavily loaded that the sides were only a few inches above the water), with four cutlasses and food and water for a few days to reach the most accessible ports, a sextant and a pocket watch, but no charts or compass. The launch could not hold all the loyal crew members, and four were detained on the Bounty by the mutineers for their useful skills; these were later released at Tahiti.
Tahiti was upwind from Bligh's initial position, and was the obvious destination of the mutineers. Many of the loyalists claimed to have heard the mutineers cry "Huzzah for Otaheite!" as the Bounty pulled away. Timor was the nearest European outpost. Bligh and his crew did make for Tofua first, to obtain supplies. There they were attacked by hostile natives and a crewman was killed. After fleeing Tofua, Bligh didn't dare stop at the next islands (the Fiji islands), as he had no weapons for defense and expected further hostile receptions.
Bligh had a well-deserved confidence in his navigational skills, which he had perfected under the instruction of Captain Cook. His first responsibility was to survive and get word of the mutiny as soon as possible to British vessels that could pursue the mutineers. Thus, he undertook the seemingly-impossible 3618 nautical mile (6701 km) voyage to Timor. In this remarkable act of seamanship, Bligh succeeded in reaching Timor after a 41-day voyage, with the only casualty being the crewman killed on Tofua. Ironically, several of the men who survived this ordeal with him soon died of sickness, possibly malaria, in the pestilential Dutch East Indies port of Batavia, as they waited for transport to England.
To this day, the reasons for the mutiny are a subject of considerable debate. Some feel that Bligh was a cruel tyrant whose abuse of the crew led members of the crew to feel that they had no choice but to take the ship from Bligh. Others feel that the crew, inexperienced and unused to the rigours of the sea and, after having been exposed to freedom and sexual excess on the island of Tahiti, refused to return to the "Jack Tars" existence of a seaman. They were "led" by a weak Fletcher Christian and were only too happy to be free from Bligh's acid tongue. They hold that the crew took the ship from Bligh so that they could return to a life of comfort and pleasure on Tahiti.
Bligh returned to London arriving in March 1790.
The Bounty's log shows that Bligh resorted to punishments sparingly. He scolded when other captains would have whipped and whipped when other captains would have hanged. He was an educated man, deeply interested in science, convinced that good diet and sanitation were necessary for the welfare of his crew. He took a great interest in his crew's exercise, was very careful about the quality of their food and insisted upon the Bounty being kept very clean. His personal morals were above reproach. He cared about the natives of Tahiti and tried (unsuccessfully) to check the spread of venereal disease among them. The flaw in this otherwise enlightened naval officer was, as J.C. Beaglehole wrote, "[Bligh made] dogmatic judgements which he felt himself entitled to make; he saw fools about him too easily...thin-skinned vanity was his curse through life... [Bligh] never learnt that you do not make friends of men by insulting them."
On the Bounty's launch, with a hopeless journey ahead of him and obliged to navigate by memory, Bligh was in his element. In the face of disaster, his courage and leadership made him capable of great things. He could rally his crew around him, and save the lives of them all. It was routine circumstances in fair weather that caused his "thin-skinned vanity" to make him temperamental and acid-tongued. Bligh's tongue-lashings over petty matters were feared far more than his infrequent lashings with a whip.
Popular fiction often confuses Bligh with Edward Edwards of the HMS Pandora, who was sent on the Royal Navy's expedition to find the mutineers and bring them to trial. Edwards was every bit the cruel man that Bligh was accused of being; the 14 men that he captured were confined in terrible conditions. When the Pandora ran aground on the Great Barrier Reef, 4 of the prisoners and 31 of the crew were killed. The prisoners would have all perished, had not some unknown crewman, more compassionate than Edwards, unlocked their cage before fleeing the doomed vessel.
In October 1790 Bligh was honourably acquitted at the court-martial inquiring the loss of the Bounty. Shortly thereafter, A Narrative of the Mutiny on board His Majesty's Ship "Bounty" was published.
Of the 10 surviving prisoners, 4 were acquitted, due to Bligh's testimony that they were non-mutineers that Bligh was obliged to leave on the Bounty due to lack of space in the launch. Two others were convicted because, while not participating in the mutiny, they were passive and did not resist. They subsequently received royal pardons. One was convicted but excused on a technicality. The remaining three were convicted and hanged.
William Bligh, pictured in his 1792 account of South Sea Mutiny voyage
After the Bounty
After a court of inquiry, Bligh went on to serve under Admiral Nelson at the Battle of Copenhagen, commanding HMS Glatton, a 56-gun ship of the line, which was experimentally fitted exclusively with carronades. After the battle, Bligh was personally praised by Nelson for his contribution to the victory. He sailed the Glatton safely between the banks while three other vessels ran aground. When Nelson feigned not to notice the signal 43 from Admiral Parker, to stop the battle and kept the signal 16 hoisted to continue the engagement, Bligh was the only captain who could see the conflicting two signals. By choosing to also display Nelson's signal, he ensured that all the vessels behind him kept fighting.
As captain of HMS Director, at the Battle of Camperdown, Bligh engaged three Dutch vessels: the Haarlem, the Alkmaar and the Vrijheid. While the Dutch suffered serious casualties, only 7 seamen were wounded on the Director.
Bligh was offered the position of Governor of New South Wales by Sir Joseph Banks and appointed in March 1805, at £2,000 per annum, twice the pay of the retiring Governor Philip Gidley King. He arrived in Sydney in August 1806, to become the fourth governor. There he suffered another mutiny, the Rum Rebellion, when, on 26 January 1808, the New South Wales Corps under Major George Johnson (a.k.a. Johnston) marched on government house and arrested him. He sailed to Hobart on the Porpoise, failed to gain support to retake control of the colony and remained effectively imprisoned on board from 1808 till January 1810.
He sailed from Hobart and arrived in Sydney on 17 January 1810 to collect evidence for the upcoming court-martial of Major George Johnson. He departed for the trial in England aboard the Porpoise on 12th May and arrived on 25 October 1810. The court-martial cashiered Johnson from the Marine Corps and British armed forces.
Afterwards, Bligh's promotion to Rear Admiral was backdated and 3 years later, in 1814, he was promoted again, to Vice Admiral of the Blue.
Bligh designed the North Bull Wall at the mouth of the River Liffey in Dublin, to ensure the entrance to Dublin Port did not silt up by a sandbar forming.
Bligh
died in Bond Street, London
on 6 December 1817 and was buried in a family plot at St. Mary's,
Lambeth. This church is now the Museum of Garden History. His tomb,
notable for its use of Coade stone, is topped by a breadfruit. A plaque
marks Bligh's house, one block east of the Museum.
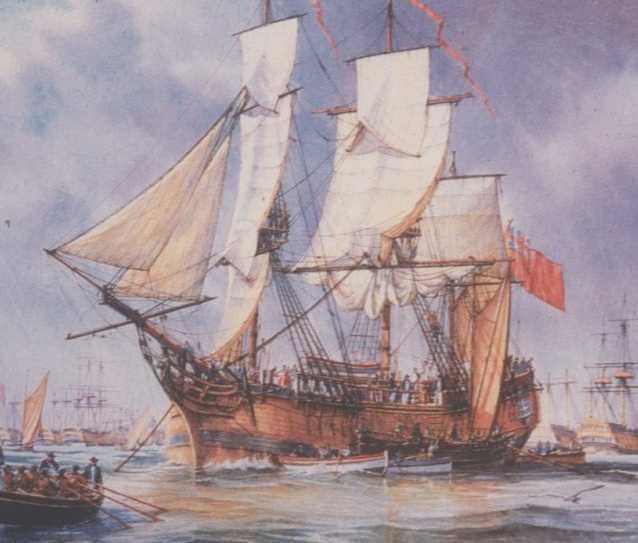
HMS Bounty sets sail
LINKS and RESOURCES
HMS Bounty - South Sea Mutiny
HMS BOUNTY | MEL GIBSON | MUTINY ON THE BOUNTY
A taste for adventure capitalists
Solar Cola - a healthier alternative
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
This
website is Copyright © 1999 & 2006
Solar Cola Ltd. The bird logo |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOMOTIVE | BLUEBIRD | ELECTRIC CARS | ELECTRIC CYCLES | SOLAR CARS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||