|

Exocoetidae is a family of marine fish in the order Beloniformes of class Actinopterygii. Fish of this family are known as flying fish. There are about sixty-four species grouped in seven to nine genera. Flying fish can make powerful, self-propelled leaps out of water into
air, where their long, wing-like fins enable gliding flight for considerable distances above the water's surface. This uncommon ability is a natural defense mechanism to evade predators.
The oldest known fossil of a flying or gliding fish, Potanichthys xingyiensis, dates back to the Middle Triassic, 235–242 million years ago. However, this fossil is not related to modern flying fish, which evolved independently about 65 million years ago.
ETYMOLOGY
The term "Exocoetidae" is not only the present scientific name for a genus of flying fish in this family, but also the general name in Latin for a
flying fish. The suffix -idae, common for indicating a family, follows the root of the Latin word exocoetus, a transliteration of the Ancient
Greek. This means literally "sleeping
outside", so named as flying fish were believed to leave the water to sleep on the shore.
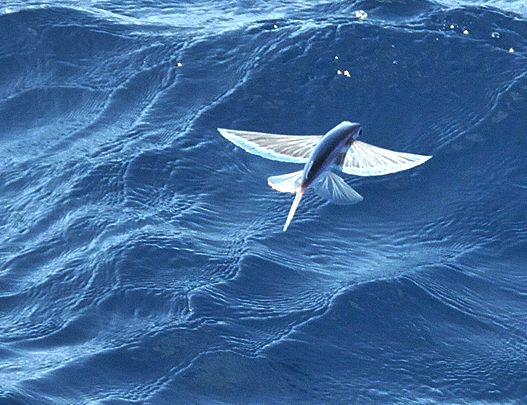

DISTRIBUTION
Flying fish live in all of the oceans, particularly in tropical and warm subtropical waters. Their most striking feature is their pectoral fins, which are unusually large, and enable the fish to hide and escape from predators by leaping out of the water and flying through air a few feet above the water's surface. Their flights are typically around 50
meters (160 ft).
To glide upward out of the water, a flying fish moves its tail up to 70 times per second. It then spreads its pectoral fins and tilts them slightly upward to provide lift. At the end of a glide, it folds its pectoral fins to reenter the sea, or drops its tail into the
water to push against the water to lift itself for another glide, possibly changing direction. The curved profile of the "wing" is comparable to the aerodynamic shape of a bird wing. The fish is able to increase its time in the air by flying straight into or at an angle to the direction of updrafts created by a combination of air and
ocean currents.
Genus Exocoetus has one pair of fins and a streamlined body to optimize for speed, while Cypselurus has a flattened body and two pairs of fins, which maximizes its time in the air. From 1900 to the 1930s, flying fish were studied as possible models used to develop airplanes.
Exocoetidae feed mainly on plankton. Predators include dolphins, tuna, marlin,
birds, squids and porpoises.

STATISTICS
In May 2008, a Japanese television crew (NHK) filmed a flying fish (dubbed "Icarfish") off the coast of Yakushima Island,
Japan. The creature spent 45 seconds in flight. The previous record was 42 seconds.
Flying fish can use updrafts at the leading edge of waves to cover distances of at least 400 m (1,300 ft). They can travel at speeds of more than 70 kilometres per hour (43 mph). Maximum altitude is 6 m (20 ft) above the surface of the sea. Some accounts have them landing on
ships' decks.
CUISINE
Flying fish are commercially fished in Japan, Vietnam and China by the method of gillnetting, and in Indonesia and India by dipnetting. In Japanese cuisine, the fish is often preserved by drying. The roe of Cheilopogon agoo, or Japanese flying fish, is used to make some types of sushi, and is known as tobiko. It is also a staple in the diet of the Tao people of Orchid Island,
Taiwan. Flying fish is part of Barbados' national dish, known as cou-cou and flying fish.
In the Solomon Islands, they are caught while flying, using nets held from outrigger canoes. They are attracted to the light of torches. Fishing is done only when there is no moonlight.
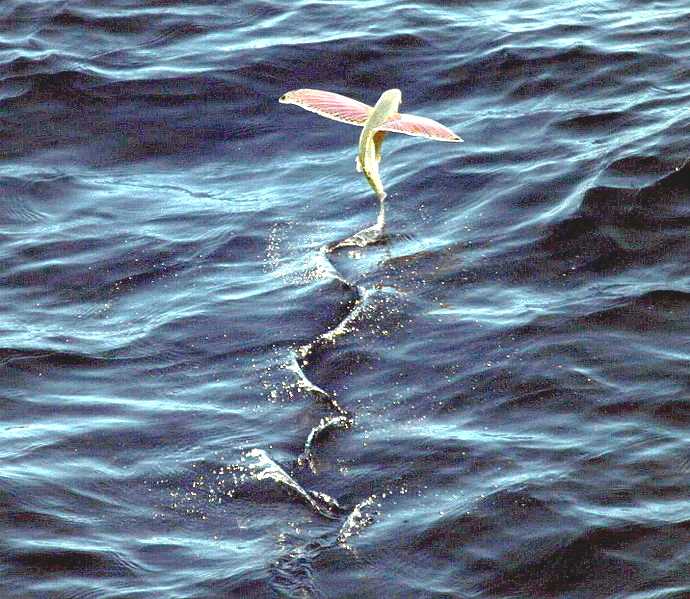

IMPORTANCE
BARBADOS
Historically, Barbados was nicknamed "the land of the flying fish", where today it is the official national fish. Once abundant, it migrated between the warm, coral-filled Atlantic Ocean surrounding the island of
Barbados and the plankton-rich outflows of the Orinoco River in Venezuela.
Just after the completion of the Bridgetown Harbor / Deep Water Harbor in Bridgetown, Barbados saw an increase of ship visits, linking the island to the world. The overall health of the coral reefs surrounding Barbados suffered due to ship-based pollution. Additionally, Barbadian overfishing pushed them closer to the Orinoco river delta, no longer returning to Barbados in large numbers. Today, the flying fish only migrate as far north as Tobago, around 120 nautical
miles (220 km; 140 mi) southwest of Barbados. Despite the change, flying fish remain a coveted delicacy.
Many aspects of Barbadian culture center around the flying fish: it is depicted on coins, as sculptures in fountains, in artwork, and as part of the official logo of the Barbados Tourism Authority. Additionally, the Barbadian coat of arms features a pelican and dolphin fish on either side of the shield, but the dolphin resembles a flying fish. Furthermore, actual artistic renditions and holograms of the flying fish are also present within the Barbadian passport.
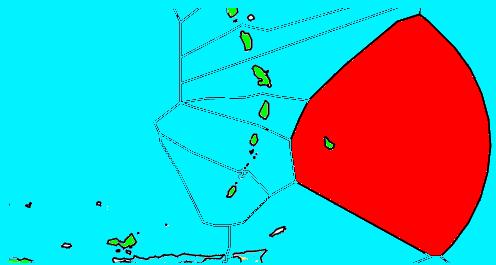
Maritime of Barbados showing (southern) U.N. instituted boundary
MARITIME DISPUTE
Barbados v. Trinidad and Tobago was a 2006 case between Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago before the Permanent Court of Arbitration in which the court resolved the maritime border dispute between the two countries.
In 1990,
Venezuela and Trinidad and Tobago signed a maritime boundary treaty. The treaty purported to assign to Trinidad and Tobago ocean territory that Barbados claimed as its own. The countries were unable to resolve their dispute for 14 years. In 2004, Barbados elected to force the issue into binding arbitration under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. The Permanent Court of Arbitration heard the case.

The court's ruling and award was issued on 11 April 2006. The boundary was set nearly midway between the land of the two island countries. Although neither country's claimed boundary was adopted by the court, the boundary that was set was closest to that claimed by Trinidad and Tobago. Both countries claimed victory after the arbitration ruling was announced.
In recent times, flying fish have also been gaining in popularity in other islands, fueling several maritime disputes. In 2006, the council of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea fixed the maritime boundaries between Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago over the flying fish dispute, which gradually raised tensions between the neighbours. The ruling stated both countries must preserve stocks for the future. Barbadian fishers still follow the flying fish southward. Flying fish remain an important part of Barbados' main national dish.
POPULAR FISH:
Please
use the Index below to navigate the Animal Kingdom:-
|
AMPHIBIANS |
Such
as frogs (class: Amphibia) |
|
ANNELIDS |
As
in Earthworms (phyla: Annelida) |
|
ANTHROPOLOGY |
Neanderthals,
Homo Erectus (Extinct) |
|
ARACHNIDS |
Spiders
(class: Arachnida) |
|
BIRDS
|
Such
as Eagles, Albatross
(class: Aves) |
|
CETACEANS
|
such
as Whales
& Dolphins
( order:Cetacea) |
|
CRUSTACEANS |
such
as crabs (subphyla: Crustacea) |
|
DINOSAURS
|
Tyranosaurus
Rex,
Brontosaurus (Extinct) |
|
ECHINODERMS |
As
in Starfish (phyla: Echinodermata) |
|
FISH
|
Sharks,
Tuna (group: Pisces) |
|
HUMANS
-
MAN |
Homo
Sapiens THE
BRAIN |
|
INSECTS |
Ants,
(subphyla: Uniramia class: Insecta) |
|
LIFE
ON EARTH
|
Which
includes PLANTS
non- animal life |
|
MAMMALS
|
Warm
blooded animals (class: Mammalia) |
|
MARSUPIALS |
Such
as Kangaroos
(order: Marsupialia) |
|
MOLLUSKS |
Such
as octopus (phyla: Mollusca) |
|
PLANTS |
Trees
- |
|
PRIMATES |
Gorillas,
Chimpanzees
(order: Primates) |
|
REPTILES |
As
in Crocodiles,
Snakes (class: Reptilia) |
|
RODENTS |
such
as Rats, Mice (order: Rodentia) |
|
SIMPLE
LIFE FORMS
|
As
in Amoeba, plankton (phyla: protozoa) |
|
|
LINKS
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Piranha
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flying_fish
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Barracuda
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manta_ray
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bluefish
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tuna

|




