|
ASIA
|
|||
|
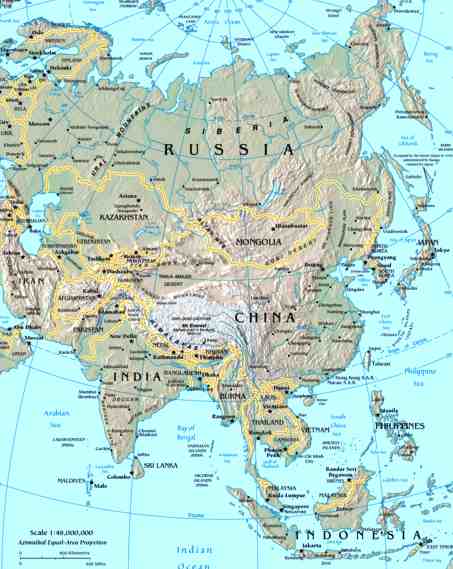
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent. It covers 8.6% of the Earth's total surface area (or 29.4% of its land area) and, with almost 4 billion people, it contains more than 60% of the world's current human population.
Chiefly in the eastern and northern hemispheres, Asia is traditionally defined as part of the landmass of Africa-Eurasia – with the western portion of the latter occupied by Europe – lying east of the Suez Canal, east of the Ural Mountains, and south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black Seas. It is bounded to the east by the Pacific Ocean, to the south by the Indian Ocean, and to the north by the Arctic Ocean.
Map of Asia
Given its size and diversity, Asia – a toponym dating back to classical antiquity – is more a cultural concept incorporating a number of regions and peoples than a homogenius, physical entity (see Subregions of Asia, Asian people).
Etymology
The word Asia originated from the Ancient Greek word "Ασία", first attributed to Herodotus (about 440 BC) in reference to Anatolia or, for the purposes of describing the Persian Wars, to the Persian Empire, in contrast to Greece and Egypt. Herodotus comments that he is puzzled as to why three women's names are used to describe one land mass (Europa, Asia, and Libya, referring to Africa), stating that most Greeks assumed that Asia was named after the wife of Prometheus but that the Lydians say it was named after Asias, son of Cotys who passed the name on to a tribe in Sardis.
Even before Herodotus, Homer knew of a Trojan ally named Asios and elsewhere he describes a marsh as ασιος (Iliad 2, 461). The Greek term may be derived from Assuwa, a 14th century BC confederation of states in Western Anatolia. Hittite assu- = "good" is probably an element in that name.
Alternatively, the ultimate etymology of the term may be from the Akkadian word (w)aṣû(m), which means "to go outside" or "to ascend", referring to the direction of the sun at sunrise in the Middle East, and also likely connected with the Phoenician word asa meaning east. This may be contrasted to a similar etymology proposed for Europe, as being from Akkadian erēbu(m) "to enter" or "set" (of the sun). However, this etymology is considered doubtful, because it does not explain how the term "Asia" first came to be associated with Anatolia, which is west of the Semitic-speaking areas, unless they refer to the viewpoint of a Phoenician sailor sailing through the straits between the Mediterranean Sea and the Black Sea.
It is interesting to note, in Icelandic Saga, ancient Teutons separated Asia from Europe by the river Tanakvisl (or Vanakvisl), which flows into the Black Sea. Eastward across the River (in Asia), so legend tells, was a land known as Asaheim or Asaland, where dwelt Odin, chief god, in his citadel named Asgard. However, Aesir and all its forms are related to Sanskrit asura and Avestan ahura, the local reflexes of the name of a class of Proto-Indo-European divine beings.
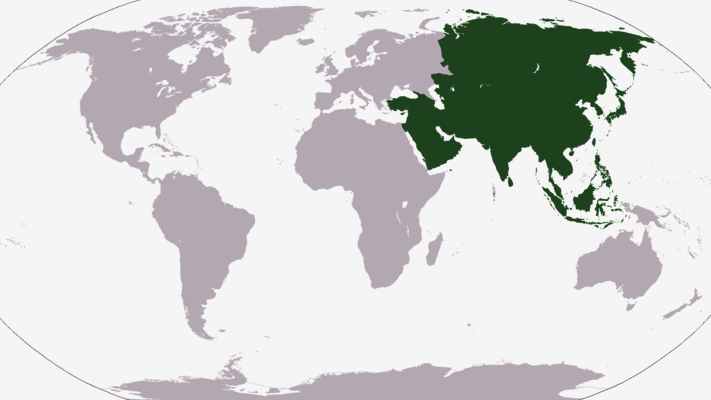
Asia - world location map
LINKS and REFERENCE
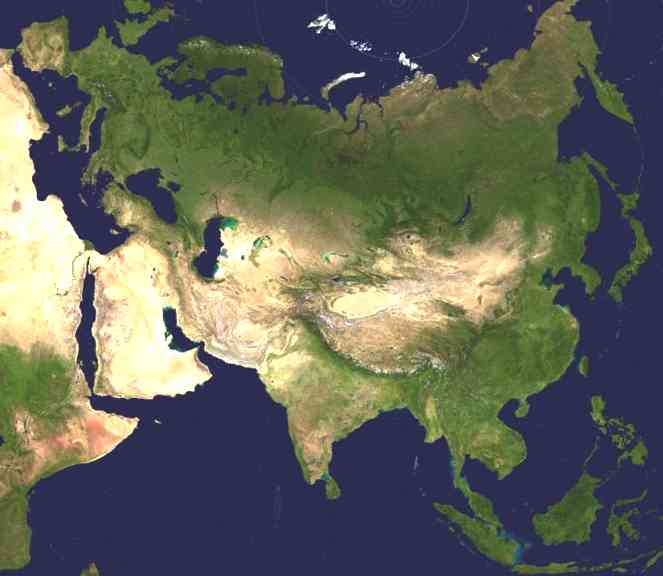
Asia satellite photograph
Solar Cola drinkers care about planet earth
.. Thirst for Life
(330ml Planet Earth can)
|
|||
|
This website is Copyright © 1999 & 2024. The bird logo and name Solar Navigator are trademarks. All rights reserved. All other trademarks are hereby acknowledged. Max Energy Limited is an educational charity.
|