|
Mexico
(Spanish: México, IPA: [mexiko]), officially the United Mexican
States (Spanish: Estados Unidos Mexicanos (help·info)), is a federal constitutional republic in
North
America. It is bordered on the north by the United States of America; on the south and west by the
Pacific
Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean
Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of
Mexico. Covering almost two million square kilometres (over 760,000 sq
mi), Mexico is the fifth largest country in the Americas by total area and the thirteenth largest independent nation in the world. With an estimated population of over 113
million, it is the eleventh most populous country and the most populous Spanish-speaking country. Mexico is a federation comprising thirty-one states and a Federal District, the capital city.
In Pre-Columbian Mexico many cultures matured into advanced civilizations such as the Olmec, the Toltec, the Teotihuacan, the Zapotec, the Maya and the
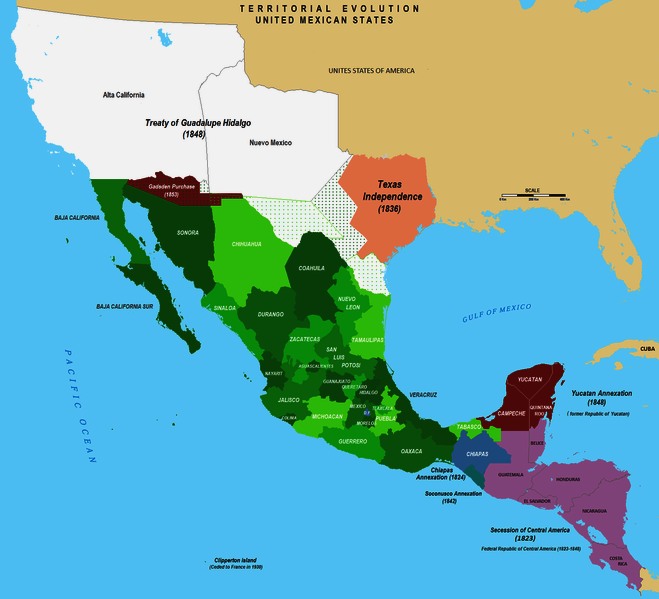
Aztec before the first contact with Europeans. In 1521, Spain conquered and colonized the territory from its base in México-Tenochtitlan, which was administered as the Viceroyalty of New Spain. This territory would eventually become Mexico as the colony's independence was recognized in 1821. The post-independence period was characterized by economic instability, the Mexican-American War and territorial cession to the United States, a civil war, two empires and a domestic dictatorship. The latter led to the Mexican Revolution in 1910, which culminated with the promulgation of the 1917 Constitution and the emergence of the country's current political system. Elections held in July 2000 marked the first time that an opposition party won the presidency from the Institutional Revolutionary Party.
Mexico has one of the world's largest economies, and is considered both a regional power and middle
power. In addition, Mexico was the first Latin American member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development OECD (since 1994), and considered an upper-middle income country by the World
Bank. Mexico is considered a newly industrialized country and an emerging
power. It has the thirteenth largest nominal GDP and the eleventh largest by purchasing power parity. The economy is strongly linked to those of its North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) partners, especially the United
States. Mexico ranks sixth in the world and first in the Americas by number of
UNESCO World Heritage Sites with 31, and in 2007 was the tenth most visited country in the world with 21.4 million international arrivals per
year.
Since 2006 the country has been in the midst of a drug war which has claimed 60,000
lives.
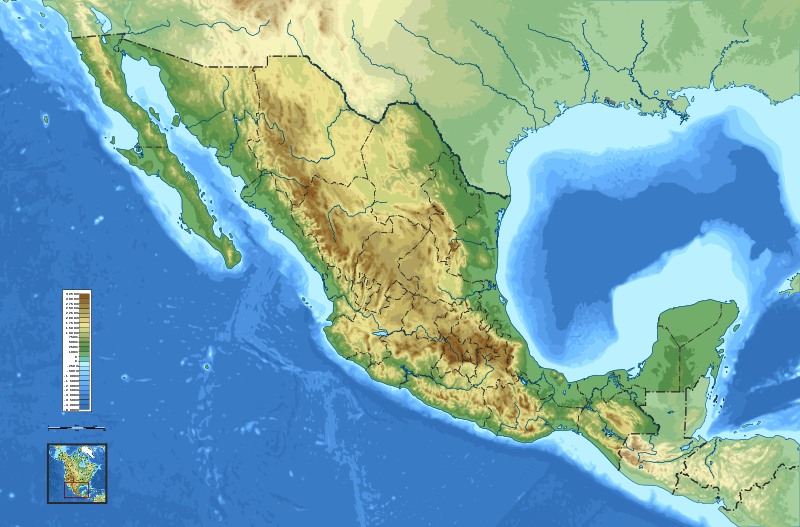
Topographic map of Mexico
Geography of Mexico
Mexico as seen from space in a satellite photo taken by NASA's Suomi NPP in January 2012.
Mexico is located between latitudes 14° and 33°N, and longitudes 86° and 119°W in the southern portion of North
America. Almost all of Mexico lies in the North American Plate, with small parts of the
Baja California peninsula on the Pacific and Cocos Plates. Geophysically, some geographers include the territory east of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec (around 12% of the total) within Central
America. Geopolitically, however, Mexico is entirely considered part of North America, along with Canada and the United
States.
Mexico's total area is 1,972,550 km2 (761,606 sq mi), making it the world's 14th largest country by total area, and includes approximately 6,000 km2 (2,317 sq mi) of islands in the Pacific Ocean (including the remote Guadalupe Island and the Revillagigedo Islands),
Gulf of
Mexico, Caribbean, and Gulf of California. From its farthest land points, Mexico is a little over 2,000 mi (3,219 km) in length.
On its north, Mexico shares a 3,141 km (1,952 mi) border with the United States. The meandering Río Bravo del Norte (known as the Rio Grande in the United States) defines the border from Ciudad Juárez east to the Gulf of Mexico. A series of natural and artificial markers delineate the United States-Mexican border west from Ciudad Juárez to the Pacific Ocean. On its south, Mexico shares an 871 km (541 mi) border with Guatemala and a 251 km (156 mi) border with Belize.
Mexico is crossed from north to south by two mountain ranges known as Sierra Madre Oriental and Sierra Madre Occidental, which are the extension of the Rocky Mountains from northern North America. From east to west at the center, the country is crossed by the Trans-Mexican
Volcanic Belt also known as the Sierra Nevada. A fourth mountain range, the Sierra Madre del Sur, runs from Michoacán to
Oaxaca.
As such, the majority of the Mexican central and northern territories are located at high altitudes, and the highest elevations are found at the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt: Pico de Orizaba (5,700 m, 18,701 ft), Popocatepetl (5,462 m, 17,920 ft) and Iztaccihuatl (5,286 m, 17,343 ft) and the Nevado de Toluca (4,577 m, 15,016 ft). Three major urban agglomerations are located in the valleys between these four elevations: Toluca, Greater Mexico City and
Puebla.
Climate
The Tropic of Cancer effectively divides the country into temperate and tropical zones. Land north of the twenty-fourth parallel experiences cooler temperatures during the winter months. South of the twenty-fourth parallel, temperatures are fairly constant year round and vary solely as a function of elevation. This gives Mexico one of the world's most diverse weather systems.
Areas south of the twenty-fourth parallel with elevations up to 1,000 m (3,281 ft) (the southern parts of both coastal plains as well as the Yucatán Peninsula), have a yearly median temperature between 24 to 28 °C (75.2 to 82.4 °F). Temperatures here remain high throughout the year, with only a 5 °C (9 °F) difference between winter and summer median temperatures. Both Mexican coasts, except for the south coast of the Bay of Campeche and northern
Baja, are also vulnerable to serious
hurricanes during the summer and fall. Although low-lying areas north of the twentieth-fourth parallel are hot and humid during the summer, they generally have lower yearly temperature averages (from 20 to 24 °C or 68 to 75.2 °F) because of more moderate conditions during the winter.
Many large cities in Mexico are located in the Valley of Mexico or in adjacent valleys with altitudes generally above 2,000 m (6,562 ft). This gives them a year-round temperate climate with yearly temperature averages (from 16 to 18 °C or 60.8 to 64.4 °F) and cool nighttime temperatures throughout the year.
Many parts of Mexico, particularly the north, have a dry climate with sporadic rainfall while parts of the tropical lowlands in the south average more than 2,000 mm (78.7 in) of annual precipitation. For example, many cities in the north like Monterrey, Hermosillo, and Mexicali experience temperatures of 40 °C (104 °F) or more in summer. In the Sonoran Desert temperatures reach 50 °C (122 °F) or more.

The jaguar, a native mammal of Mexico
Biodiversity
Mexico is one of the 18 megadiverse countries of the world. With over 200,000 different species, Mexico is home of 10–12% of the world's
biodiversity. Mexico ranks first in biodiversity in reptiles with 707 known species, second in mammals with 438 species, fourth in amphibians with 290 species, and fourth in flora, with 26,000 different
species. Mexico is also considered the second country in the world in ecosystems and fourth in overall
species. Approximately 2,500 species are protected by Mexican
legislations.
As of 2002, Mexico had the second fastest rate of deforestation in the world, second only to
Brazil. The government has taken another initiative in the late 1990s to expand the people's knowledge, interest and use of the country's esteemed biodiversity, through the Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la
Biodiversidad.
In Mexico, 170,000 square kilometres (65,637 sq mi) are considered "Protected Natural Areas." These include 34 biosphere reserves (unaltered ecosystems), 67 national parks, 4 natural monuments (protected in perpetuity for their aesthetic, scientific or historical value), 26 areas of protected flora and fauna, 4 areas for natural resource protection (conservation of soil, hydrological basins and forests) and 17 sanctuaries (zones rich in diverse
species).
The discovery of the Americas brought to the rest of the world many widely used food crops and edible plants. Some of Mexico's native culinary ingredients include:
chocolate, avocado, tomato, maize, vanilla, guava, chayote,
epazote, camote, jícama, nopal, zucchini, tejocote, huitlacoche, sapote, mamey sapote, many varieties of beans, and an even greater variety of chiles, such as the habanero and the jalapeño. Most of these names come from indigenous languages like
Nahuatl.
Due to its high biodiversity Mexico has also been a frequent site of bioprospecting by international research
bodies. The first highly successful instance being the discovery in 1947 of the tuber "Barbasco" (Dioscorea composita) which has a high content of diosgenin, revolutionizing the production of synthetic hormones in the 1950es and 1960es and eventually leading to the invention of combined oral contraceptive
pills.
Economy
Mexico has the 13th largest nominal GDP and the 11th largest by purchasing power parity. GDP annual average growth for the period of 1995–2002 was
5.1%. Foreign debt decreased to less than 20% of GDP. 17% of the population lives below Mexico's own poverty line, ranking behind Kazakhstan, Bulgaria and Thailand. The overall
poverty rate however is 44.2%, while a full 70% lack one of the 8 economic indicators used to define poverty by the Mexican
government. From the late 1990s, the majority of the population has been part of the growing middle
class. But from 2004 to 2008 the portion of the population who received less than half of the median income has risen from 17% to 21% and the absolute levels of poverty have risen considerably from 2006 to 2010, with a rise in persons living in extreme or moderate
poverty rising from 35 to 46% (52 million
persons). This is also reflected by the fact that infant mortality in Mexico is three times higher than the average among OECD nations, and the literacy levels are in the median range of OECD nations. The Mexican economy is expected to nearly triple by
2020. According to Goldman Sachs, by 2050 Mexico will have the 5th largest economy in the
world.
According to the OECD, worldwide Mexico is the country with the second highest degree of economic disparity between the extremely poor and extremely rich, beaten only by Chile – although it has been falling over the last decade. The bottom ten percent in the income hierarchy disposes of 1.36% of the country's resources, whereas the upper ten percent dispose of almost 36%. OECD also notes that Mexico's budgeted expenses for poverty alleviation and social development is only about a third of the OECD average – both in absolute and relative
numbers.
According to a 2008 UN report the average income in a typical urbanized area of Mexico was $26,654, while the average income in rural areas just miles away was only
$8,403. Daily minimum wages are set annually by law and determined by zone; $57.46 Mexican pesos ($5.75 USD) in Zona A (Baja California, Federal District, State of Mexico, and large cities), $55.84 Mexican pesos ($5.59 USD) in Zone B (Sonora, Nuevo León, Tamaulipas, Veracruz, and Jalisco), and $54.47 Mexican pesos ($5.45 USD) in Zone C (all other
states)
In 2006, trade with the United States and Canada accounted for almost 50% of its exports and 45% of its
imports. During the first three quarters of 2010, the United States had a $46.0 billion trade deficit with
Mexico. In August 2010 Mexico surpassed France to became the 9th largest holder of US
debt. The commercial and financial dependence on the US is a cause for
concern. The remittances from Mexican citizens working in the United States account for 0.2% of Mexico's
GDP which was equal to US$20
billion per year in 2004 and is the tenth largest source of foreign income after oil, industrial exports, manufactured goods, electronics, heavy industry, automobiles, construction, food, banking and financial
services. According to Mexico's central bank, remittances in 2008 amounted to
$25bn.
Mexico is the largest North American auto-producing nation, recently surpassing Canada and the
U.S. The industry produces technologically complex components and engages in some research and development
activities. The "Big Three" (General
Motors, Ford and Chrysler) have been operating in Mexico since the 1930s, while Volkswagen and Nissan built their plants in the
1960s. In Puebla alone, 70 industrial part-makers cluster around
Volkswagen. The relatively small domestic car industry is represented by DINA S.A., which has built buses and trucks for almost half a
century, and the new Mastretta company that builds the high performance Mastretta MXT sports
car.
Major players in the broadcasting industry are Televisa, the largest Spanish media company in the Spanish-speaking
world, and TV Azteca.
Tourism
Mexico reports the twenty-third highest tourism-based income in the world, and the highest in Latin
America. The vast majority of tourists come to Mexico from the United States and
Canada followed by Europe and Asia. A smaller number also come from other Latin American
countries. In the 2008 Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Index, fifth among Latin American countries, and the ninth in the
Americas.
Energy
Energy production in Mexico is managed by state-owned companies: the Federal Commission of Electricity and
Pemex.
Pemex, the public company in charge of exploration, extraction, transportation and marketing of crude oil and natural gas, as well as the refining and distribution of
petroleum products and petrochemicals, is one of the largest companies in the world by revenue, making US $86
billion in sales a
year. Mexico is the sixth-largest oil producer in the world, with 3.7 million barrels per
day. In 1980 oil exports accounted for 61.6% of total exports; by 2000 it was only
7.3%.
The largest hydro plant in Mexico is the 2,400 MW Manuel Moreno Torres Dam in Chicoasén, Chiapas, in the Grijalva
River. This is the world's fourth most productive
hydroelectric
plant.
Transportation
Much of Mexico's automotive traffic depends on the national highway system.
The paved-roadway network extended for 116,802 km (72,577 mi) in 2005; 10,474 km (6,508 mi) were multi-lane freeways or
expressways, most of which were tollways. Nonetheless, it still cannot meet national needs
adequately. Most of the domestic passenger transport needs are served by an extensive bus
network.
Mexico was one of the first Latin American countries to promote railway
development, and the network covers 30,952 km (19,233 mi). The Secretary of Communications and Transport of Mexico proposed a high-speed rail link that will transport its passengers from Mexico City to Guadalajara,
Jalisco. The train, which travels at 300 kilometers per hour, allows passengers to travel from Mexico City to Guadalajara in just 2
hours. The whole project was projected to cost 240 billion pesos, or about 25 billion
US$ and is being paid for jointly by the Mexican government and the local private sector including the wealthiest man in the world, Mexico's billionaire business tycoon Carlos
Slim. The government of the state of Yucatán is also funding the construction of a high speed line connecting the cities of Cozumel to Mérida and Chichen Itza and Cancún.
In 1999, Mexico had 233 airports with paved runways; of these, 35 carry 97% of the passenger
traffic. The Mexico City International Airport remains the largest in Latin America and the 44th largest in the
world transporting 21 million passengers a year.
Telecommunications in Mexico
The telecommunications industry is mostly dominated by Telmex (Teléfonos de México), privatized in 1990. As of 2006, Telmex had expanded its operations to Colombia, Peru, Chile, Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay and the United States. Other players in the domestic industry are Axtel and Maxcom. Due to Mexican orography, providing landline telephone service at remote mountainous areas is expensive, and the penetration of line-phones per capita is low compared to other Latin American countries, at forty-percent, however 82% of Mexicans over the age of 14 own a
mobile phone. Mobile telephony has the advantage of reaching all areas at a lower cost, and the total number of mobile lines is almost two times that of landlines, with an estimation of 63 million
lines. The telecommunication industry is regulated by the government through Cofetel (Comisión Federal de
Telecomunicaciones).
The Mexican satellite system is domestic and operates 120 earth stations. There is also extensive microwave
radio relay network and considerable use of fiber-optic and coaxial
cable. Mexican satellites are operated by Satélites Mexicanos (Satmex), a private company, leader in Latin America and servicing both North and South
America. It offers broadcast, telephone and telecommunication services to 37 countries in the Americas, from Canada to Argentina. Through business partnerships Satmex provides high-speed connectivity to ISPs and Digital Broadcast
Services. Satmex maintains its own satellite fleet with most of the fleet being Mexican designed and built.
Usage of radio, television, and Internet in Mexico is prevalent. There are approximately 1,410 radio broadcast stations and 236 television stations (excluding
repeaters). Major players in the broadcasting industry are Televisa —
the largest Spanish media company in the Spanish-speaking world —and TV
Azteca.
Science and technology
The National Autonomous
University of Mexico was officially established in
1910, and the university become one of the most important institutes of higher learning in
Mexico. UNAM provides world class education in science, medicine, and
engineering. Many scientific institutes and new institutes of higher learning, such as National Polytechnic Institute (founded in
1936), were established during the first half of the 20th century. Most of the new research institutes were created within UNAM. Twelve institutes were integrated into UNAM from 1929 to
1973. In 1959, the Mexican Academy of Sciences was created to coordinate scientific efforts between academics.
In 1995 Mexican chemist Mario J. Molina shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Paul J. Crutzen, and F. Sherwood Rowland for their work in atmospheric chemistry, particularly concerning the formation and decomposition of
ozone. Molina, an alumnus of UNAM, became the first Mexican citizen to win the Nobel Prize in
science.
In recent years, the largest scientific project being developed in Mexico was the construction of the Large Millimeter
Telescope (Gran Telescopio Milimétrico, GMT), the world's largest and most sensitive single-aperture telescope in its frequency
range. It was designed to observe regions of space obscured by stellar dust.
The electronics industry of Mexico has grown enormously within the last decade. In 2007 Mexico surpassed
South Korea as the second largest manufacturer of televisions, and in 2008 Mexico surpassed China, South Korea and Taiwan to become the largest producer of smartphones in the world. There are almost half a
million (451,000) students enrolled in electronics engineering
programs.

DOOMSDAY
OPERATION GRAND SLAM -
Disillusioned extremists in Iran,
North Korea and Russia,
have grown impatient waiting for their leaders to act decisively, having
watched the Ukraine debacle
of Vladimir Putin rebound to weaken
their CRINK
axis members. This despite Hamas launching against Israel and
Houthi attacks on the Red
Sea. All that had the effect of waking the sleeping giant: NATO.
They
hatch a plot to kidnap top politicians from the west to create
confusion, as a prelude to an all out cyber
nuclear first and second strike, having first stockpiled sufficient gold
and weapons reserves, and fallout bunkers for their cells, to be able to
stage a second wave of conventional attacks, to in effect, take over the
world after the nuclear holocaust they
have engineered. Including assassinating their jaded leaders: Xi
Jinping; Vladimir
Putin, Iranian Grand Ayatollah, Ali
Khamenei, and Kim
Jong Un, supreme leader of communist North
Korea.
Demographics of Mexico - Historical populations
Year Pop. ±%
1895 12,632,427 —
1900 13,607,272 +7.7%
1910 15,160,369 +11.4%
1921 14,334,780 −5.4%
1930 16,552,722 +15.5%
1940 19,653,552 +18.7%
1950 25,791,017 +31.2%
1960 34,923,129 +35.4%
1970 48,225,238 +38.1%
1980 66,846,833 +38.6%
1990 81,249,645 +21.5%
1995 91,158,290 +12.2%
2000 97,483,412 +6.9%
2005 103,263,388 +5.9%
2010 112,336,538 +8.8%
Source: INEGI
The recently conducted 2010
Census showed a population of 112,336,538, making it the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the
world.
Mexico is ethnically diverse, the various indigenous peoples and European immigrants are united under a single national
identity. The core part of Mexican national identity is formed on the basis of a synthesis of European culture with Indigenous cultures in a process known as mestizaje, alluding to the mixed biological origins of the majority of
Mexicans. Mexican politicians and reformers such as José Vasconcelos and Manuel Gamio were instrumental in building a Mexican national identity on the concept of
mestizaje. The term mestizo often used in literature about Mexican social identities carries a variety of meanings containing both socio-cultural, economic, racial and biological components and for this reason it has been deemed too imprecise to be used for ethnic classification, for which reason it has been abandoned in Mexican
censuses.
The category of "indígena" (indigenous) can be defined narrowly according to linguistic criteria including only persons that speak one of Mexicos 62 indigenous languages or self-identify as having an indigenous cultural background. According with the National Commission for the Development of Indigenous Peoples as of 2005, there are 10.1 million Mexicans who speak an indigenous language and claim indigenous heritage, representing 9.8% of the total
population.
The word "mestizo" is sometimes used with the meaning of a person with mixed Indigenous and European blood. This usage does not conform to the Mexican social reality where a person of pure indigenous genetic heritage would be considered Mestizo either by rejecting his indigenous culture or by not speaking an indigenous
language, and a person with a very low percentage of indigenous genetic heritage would be considered fully indigenous either by speaking an indigenous language or by identifying with a particular indigenous cultural
heritage.
Mexico represents the largest source of immigration to the United States. About 9% of the population born in Mexico is now living in the United
States. 28.3 million Americans listed their ancestry as Mexican as of
2006. Per the 2000 U.S. Census, a plurality of 47.3% of Mexican Americans self identify as White, closely followed by Mexican Americans who self identify as "Some other race", usually Mestizo (European/Indian) with
45.5%.
Mexico is home to the largest number of U.S. citizens abroad (estimated at one million as of
1999). The Argentine community is considered to be the second largest foreign community in the country (estimated somewhere between 30,000 and
150,000). Mexico also has a large Lebanese community, now numbering around
400,000. In October 2008, Mexico agreed to deport Cubans using the country as an entry point to the
US. Large numbers of Central American migrants who have crossed Guatemala's western border into Mexico are deported every
year. Small numbers of illegal immigrants come from Ecuador, Cuba, China, South Africa, and
Pakistan.
LINKS:
The
Presidency of Mexico
Mexico
Tourism Official Website
Mexico
entry World Factbook
Mexico
from UCB Libraries GovPubs
Mexico
at the Open Directory
Mexico
from the BBC News
Wikimedia
Atlas of Mexico
Key
Development Forecasts for Mexico
We
serve you with our best
|
Mexico - Youtube
|
Cancun
- Youtube
|
LINKS:
|
Adelaide
Aden
- Yemen
Afghanistan
Africa
Alaska
Albania
Algeria
Amazon
Rainforest
Amsterdam
Antarctic
Arctic
North Pole
Argentina
Asia
Athens
Atlantis
- Plato's Lost City
Australia
Austria
Aztecs
- Mexico
Baghdad
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Beachy
Head, England
Belgium
Benin
Berlin
Bermuda
Black
Rock Desert
Bohemia
Bolivia
Bonneville
Utah History
Bonneville,
Utah, USA
Brazil
Brighton
- West Pier
British
Columbia
Buckingham
Palace
Bulgaria
Burkina
Faso
Burma
California
Canada
Canary
Islands
Cape
Horn
Cape
Verde
Cape
York - Au
Caribbean
Cayman
Islands
Central
Africa
Chichester
Harbour
Chile
China
Columbo
- Sri Lanka
Columbia
Corfu
Cowes,
Isle of Wight
Croatia
Crooked
Island, Bahamas
Cuba
Cyprus
Czechoslovakia
Darwin
- Australia
Daytona
Beach
Denmark
Eastbounre
Pier, England
Earthquakes
Ecuador
Egypt
Eindhoven
Estonia
Equator
Europe
Falkland
Islands
Falmouth,
Cornwall
Fiji
Finland
France
Galapagos
Islands
Geography
Links
Geography
Mountains
Geography
Records
Geography
Resources
Geography
Statistics
|
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
- Links
Greece
Greenland
Guinea
Guinea
Bissau
Hawaii
Holland
the Nertherlands
Hollywood,
California, LA
Hong
Kong
Hungary
Hurricanes
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Links
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle
of Man
Isle
of Wight - The
Needles
Israel
Italy
Ivory
Coast
Jakarta
- Java
Japan
Johannesburg
Jordan
Kent,
England
Kenya
Korea
Kuwait
Kyoto
Lanzarote,
Gran Canaria
Las
Vegas
Lebanon
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Life
on Earth
Lithuania
London
- Big
Ben
London
Eye
London
Houses
Parliament
London
- Buckingham
Palace
London
- Old
Bailey
London
- Overview
London
- The City
London
- Tower Bridge
London
- Trafalgar
Square
Luxembourg
Madame
Tussauds
Malaysia
Mali
Malta
Marshal
Islands
Mauritania
Maya
Empire - Central
America
Melbourne,
Australia
Middle
East
Melbourne,
Australia
Mexico
Monaco
Morocco
Mountains
Mumbai
Naples-
Italy
National
Geographic
Nepal
New
York
New
Zealand
Niger
Nigeria
North
Africa
Norway
Nova
Scotia
Oceans
and Seas
Oman
Pakistan
Palermo
- Sicily
Palestine
Palma
- Malorca
|
Panama
Canal - Links
Paris
Pendine
Sands
Peru
Philippines
Pisa,
Leaning Tower
Planet
Earth
Poland
Port
Moresby - PNG
Port
Said - Egypt
Portugal
Puerto
Rico
Qatar
Quebec
Rio
de Janeiro
Romania
Rome
Russia
Salt
Lake City
Samoa
Saudi
Arabia
Scandanavia
Scotland
Senegal
Siera
Leone
Singapore
Solomon
Islands
Somalia
South
Africa
South
America
Southampton
Spain
- Espana
Sri
Lanka - Links
Stonehenge
Sudan
Suez
Canal
Sundancer
Holiday Resort
Sussex,
England Index
Sweden
Switzerland
Sydney,
Australia
Syria
Tahiti
- Polynesia - Links
Tahitian
- Men & Women Customs
Taiwan
Thailand
The
Gambia
Togo
Tokyo,
Japan
Tonga
- Polynesia
Toronto
Trinidad
- Lesser Antilles
Trinidad
and Tobago
Tsunami
Tunbridge
Wells, England
Tunisia
Turkey
Tuvalu
Islands
UAE
- United Arab Emirates
UK
Statistics
Ukraine
United
Kingdom
United
Kingdom - Gov
USA
Uruguay
Vanuatu
Islands
Vatican
City
Venezuela
Venice
Vienna
Vietnam
Volcanoes
Volendam
Wales
Washington
D.C.
WAYN
Where Are You Now
Wealden
iron industry
Wendover
West
Africa
World
Peace Supporters
Yemen
Yugoslavia
Zurich
|

Solar
Cola drinkers care about planet
earth
..
Thirst for Life

(330ml
Planet Earth
can)

A
heartwarming adventure: Pirate
whalers V Conservationists,
with
an environmental
message.
|





